Exterior scaffolding Setup instructions
Setup instructions
Scaffolding should be erected by at least two people. One person should be knowledgeable in erecting scaffolding to supervise the work. These step-by-step instructions are only a general guide. The following example is based on building a scaffolding that is 7 x 5 ft. by 1 frame high.
 1
1
Select and prepare the ground area. Place suitable sills and make sure there are no holes under the sills. Select the equipment you need and place it near the work area. Put the adjustable levelling jack plates on the sills in the location that matches your scaffold dimensions. Do not secure the bases to the sills at this step.
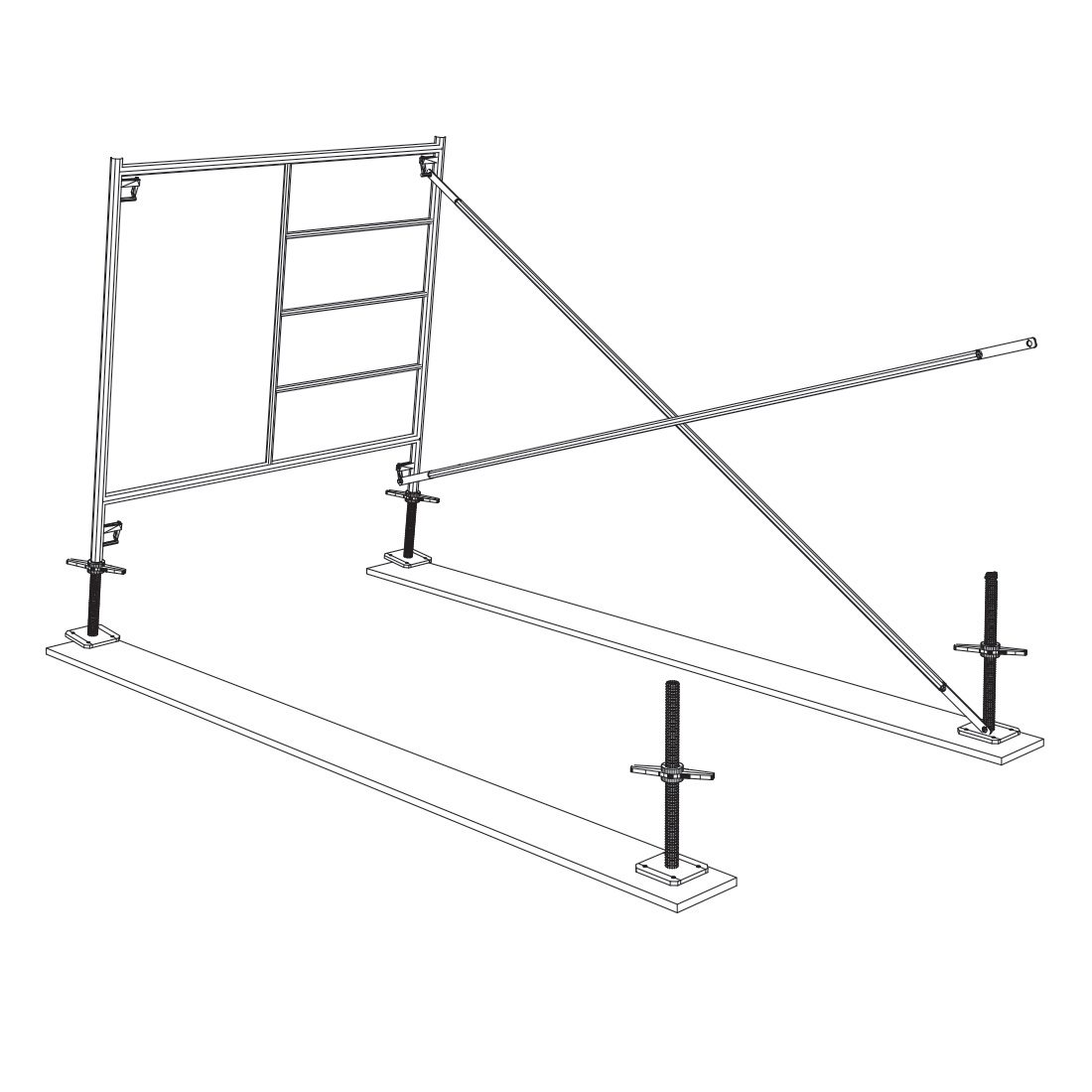 2
2
Adjust the nuts of the levelling jack, starting at the highest point of the ground level. The nuts at the highest ground level should be set to 3-6 inches from the top of the sill, depending on the slope. Place the first frame onto the base at the highest point. Connect the first cross brace to the frame. Allow the frame to lean slightly forward and rest on the sill while you prepare for the next frame to be installed.
 3
3
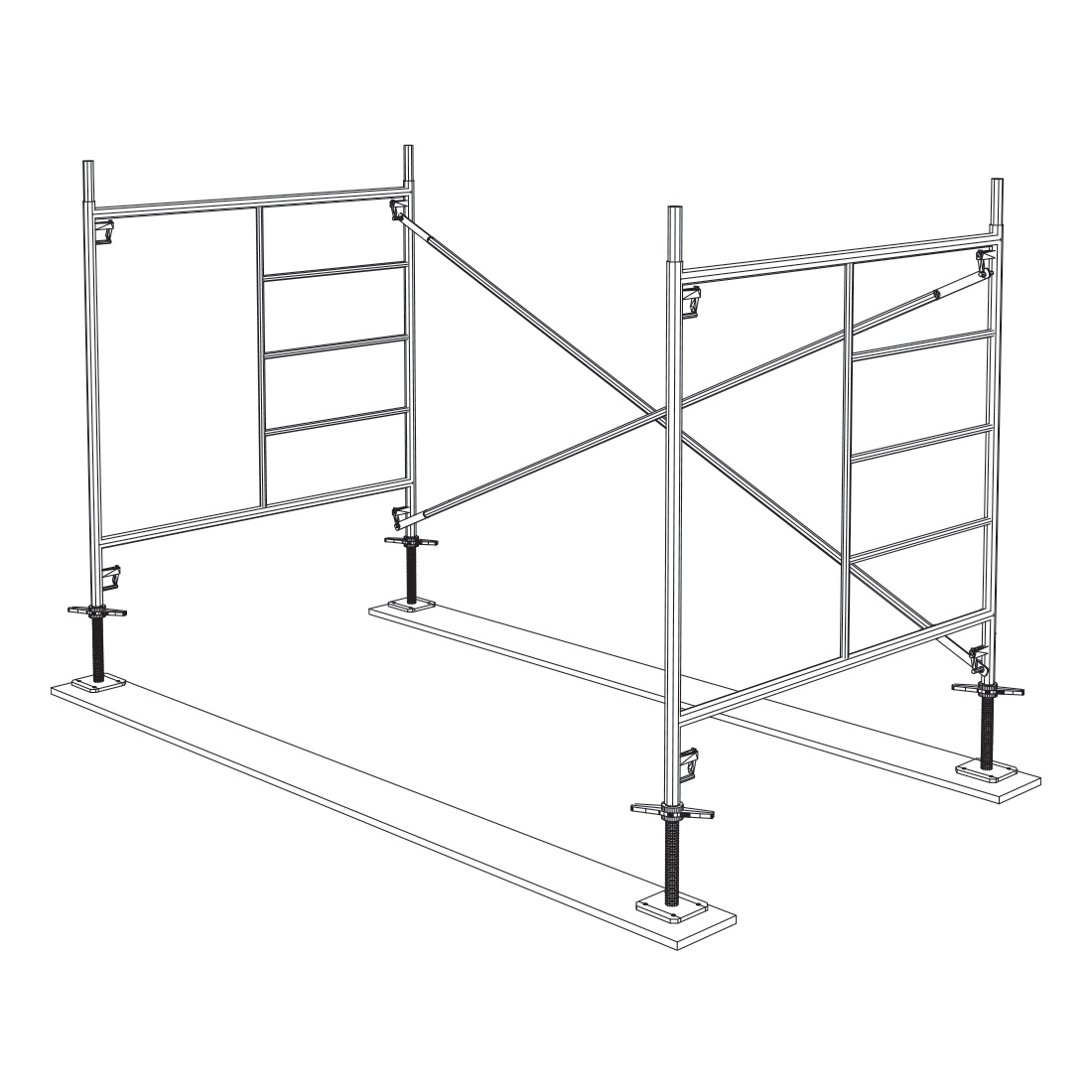
Install the second frame onto the levelling jack. Secure the first cross brace to the second frame.
 4
4
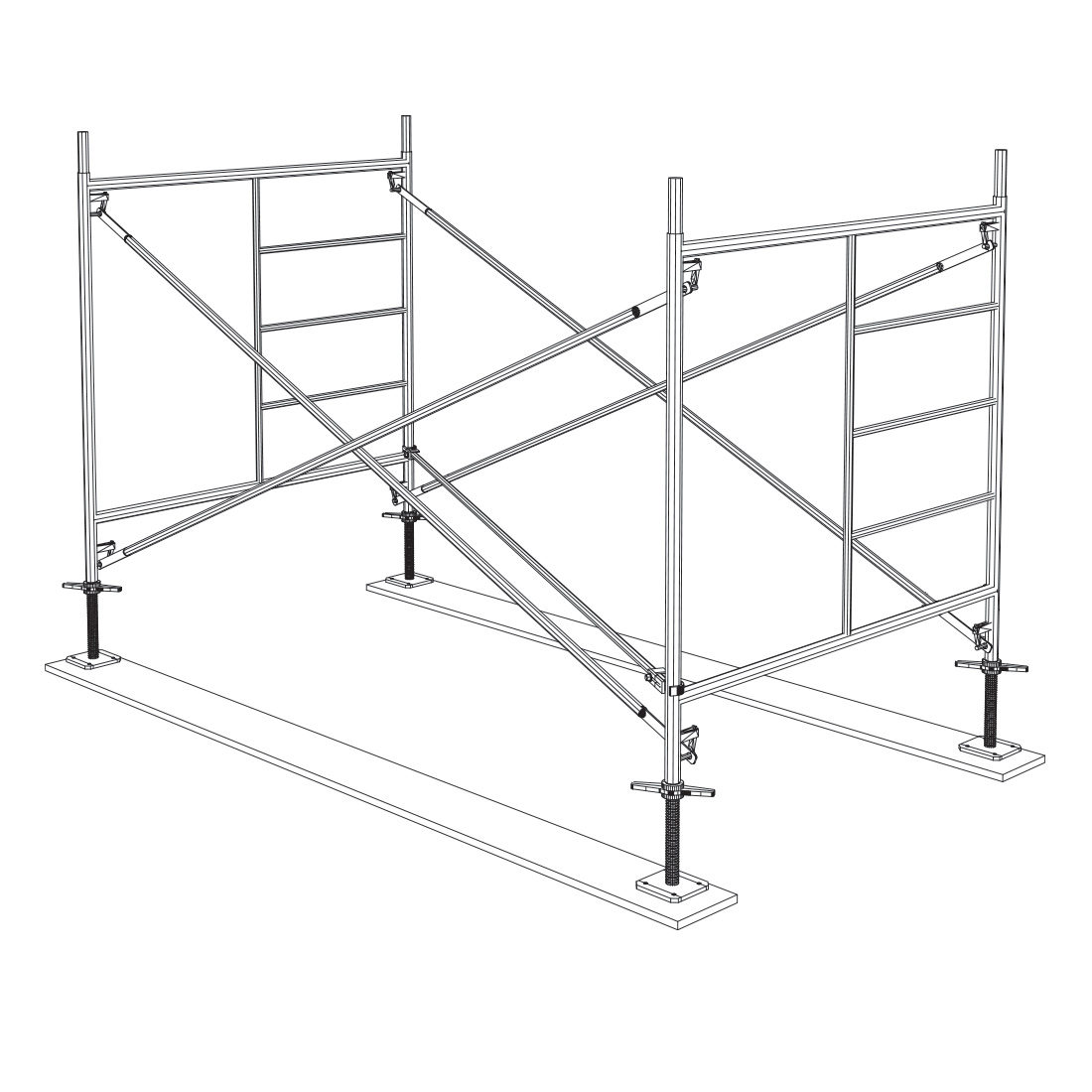
Install the second cross brace to both frames. Next, you need to level and plumb the scaffolding. Start at the highest point of the scaffolding. If possible, use the levelling jack to bring the highest corner down closer to the sill. Next, bring all four corners up to that point. If the bottom cross braces of each frame are level with each other, then frames should also be plumb. Install the diagonal brace to keep the scaffolding square. Check the level again and plumb if necessary. Fasten the levelling jack to the sills with either nails or screws.
 5
5
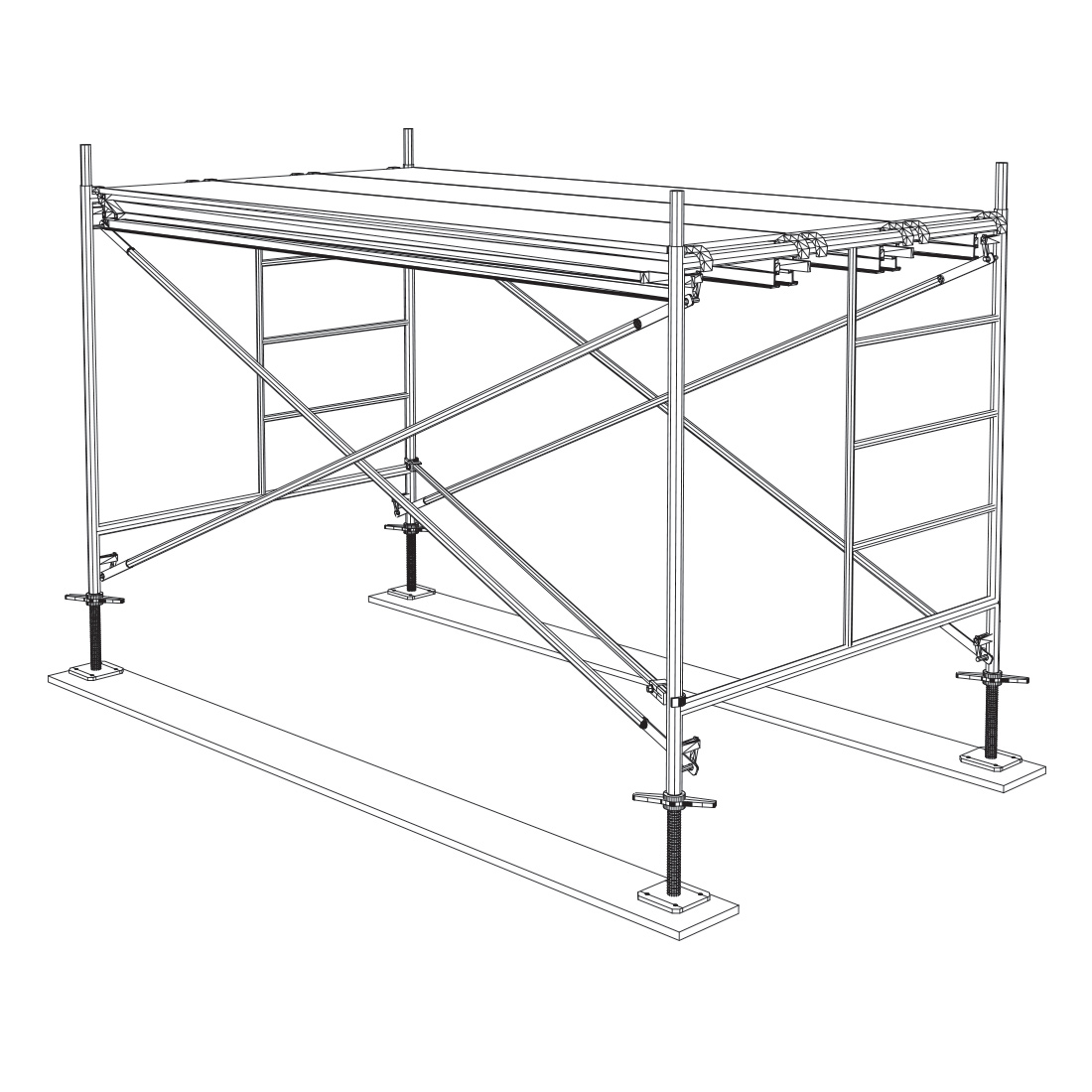
Install the deck, which may be an all aluminium platform or with wood deck or scaffold planks. If using wooden planks, they must extend beyond the supporting points at least 6 inches but not more than 12 inches. Secure the deck so it cannot move.
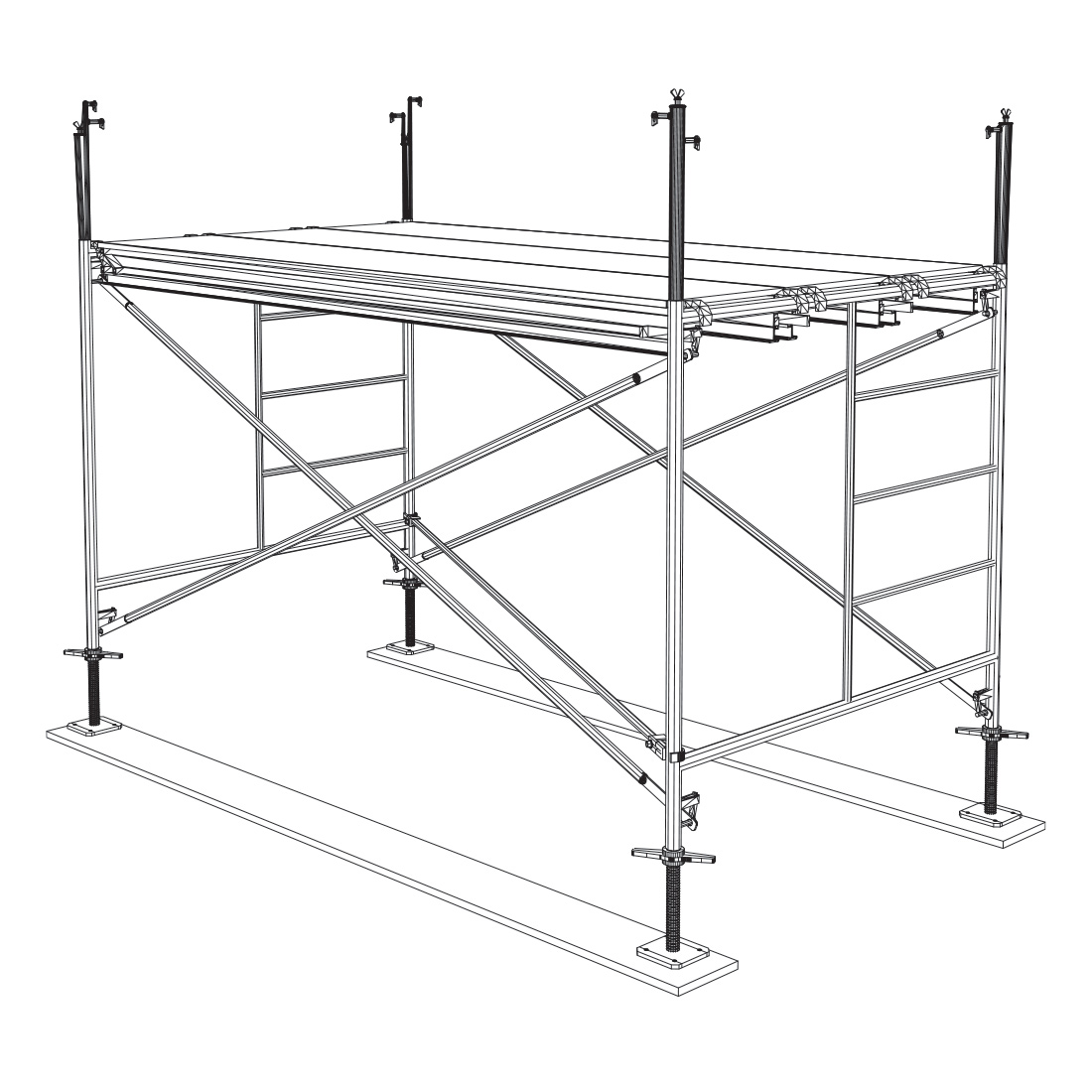 6
6
Install the guardrail posts onto the coupling pins seated in the top of the frames. Put a pig tail lock through the top and bottom of each coupling pin to avoid any separation.
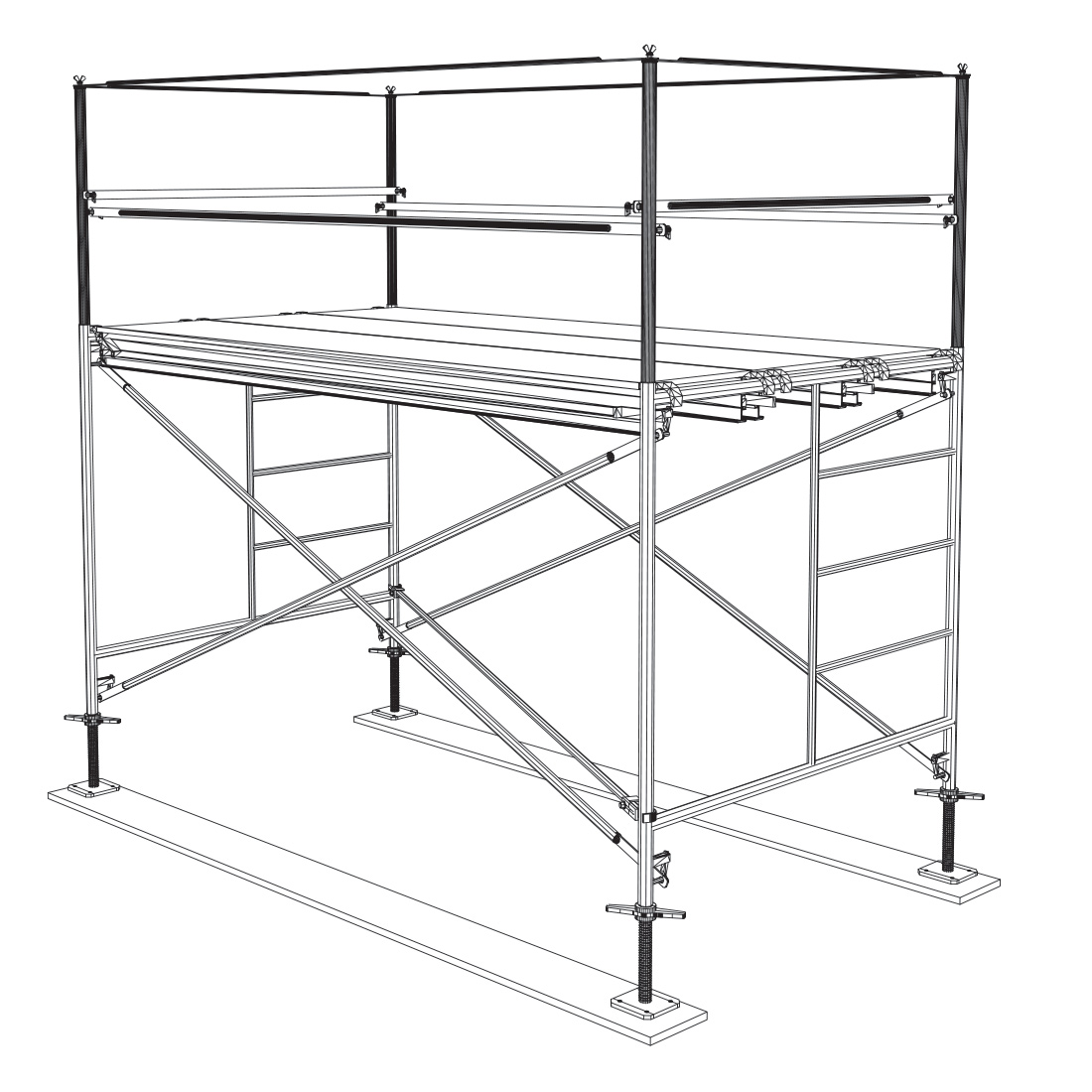 7
7
Attach the guardrails to the posts on all the exposed sides.
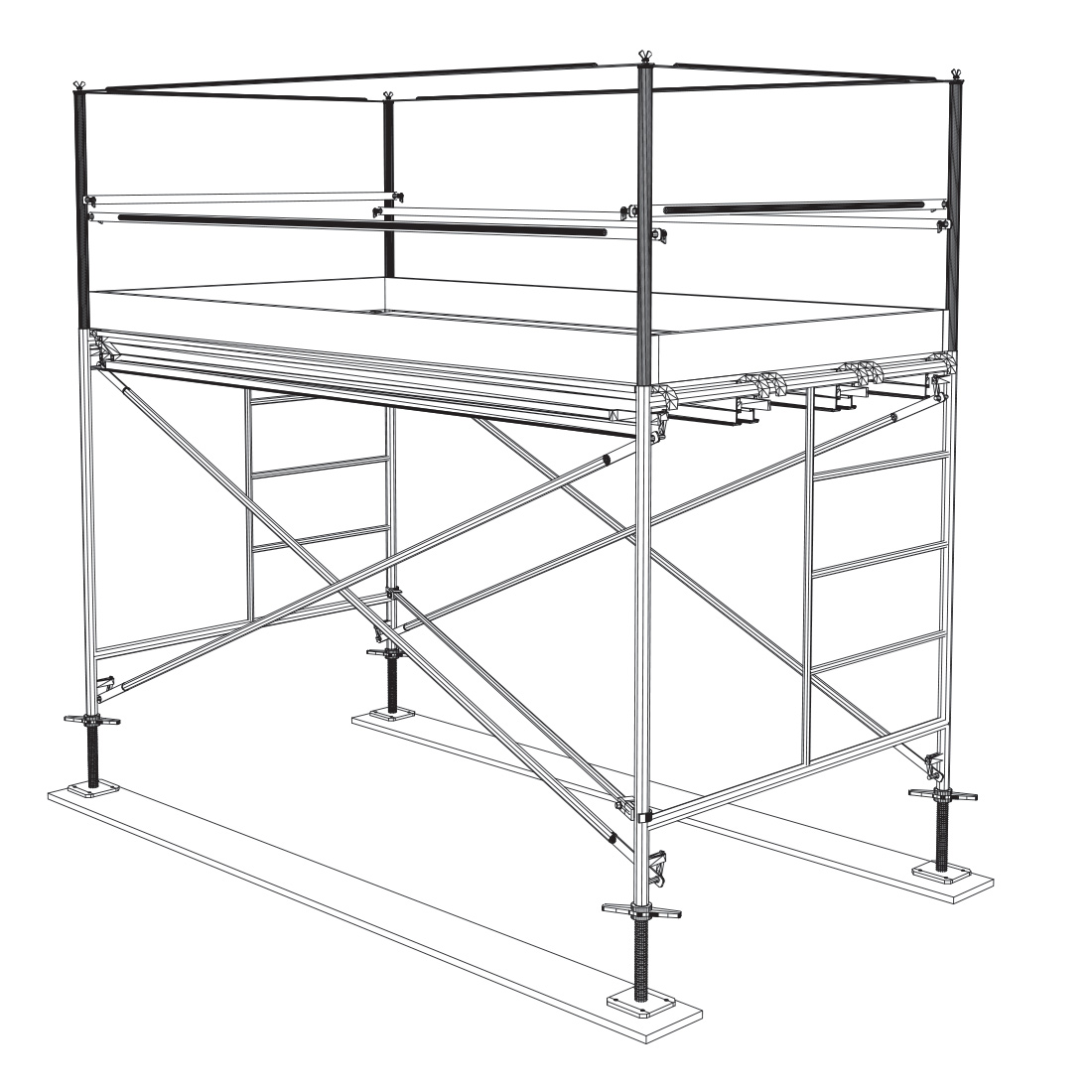 8
8
Install toeboards as required. The gap between the bottom of the toeboard and the top of the platform must not be more than 1/2 inches.
Safety Guidelines
The product or assembly variants shown in these instructions for assembly and use may be subject to local regulations. The product user bears the responsibility for compliance with such regulations, if there is a conflict between this guidelines and the local regulations, local regulations shall supersede these guidelines.
- Requirements for access frame scaffolding
- A scaffold must be erected, altered, and dismantled by qualified workers or under the direct supervision of a qualified person. The qualified person must ensure that the erection is carried out properly, and that the correct components and materials are being used. All equipment must be inspected before use to ensure that it is in good repair and suitable for the intended use.
- The base must be firm and level enough to support the load of scaffolding, workers, and materials. Sills and base plates are required on any soil or unstable ground condition, or where any levelling adjustment is needed. The sill must be sound, rigid, and capable of supporting the maximum loads without settlement or deformation.
- Levelling jack base must be adjusted within the limits specified by the local regulation.
- The frames must be plumb and level and spaced to adequately support the loads.
- If uplift could cause the components to separate, locking pins must be used and the components secured. Uplift might be caused by the action of wind on a secured deck or by the leverage action of a cantilever side bracket on the scaffolding. All joints must be pinned on rolling scaffoldings and free-standing towers.
- With a rolling scaffolding or free-standing tower, the platform height must not exceed three times its smallest base dimension (3 to 1 rule). A scaffolding built above the 3 to 1 rule must be effectively guyed or secured to a building or structure to prevent overturning. The guying of a scaffolding may require the direction of a professional engineer.
- A scaffolding built above the 3 to 1 rule must be effectively guyed or secured to a building or structure to prevent overturning. The guying of a scaffolding may require the direction of a professional engineer.
- Guardrails must be installed on all open sides of the platform where a person could fall a distance of 10 ft. or more. The top rail must be placed 40-44 in. above the work surface. An intermediate rail must be placed halfway between the top rail and the toeboard, if one is provided, or halfway between the top rail and the work surface if no toeboard is provided.
- Toeboards must be installed on all the open sides of a platform where it is possible for tools and or materials to roll off. The top of the toeboard must be at least 4 in. above the platform. If loose materials are to be stacked above the height of the toeboard, then the toeboard must be increased in height or mesh panels must be installed to prevent materials from falling off the scaffolding.
- Before erecting access frame scaffolding
- What will the scaffolding be used for? For example, light duty (one or two workers; painting a wall), or heavy duty (several tradespersons, with large and heavy materials on the platform)?
- How high will the scaffolding be? Will it be erected in one operation or as the work progresses?
- Is the ground firm? Can it support the loads from the scaffolding, workers, and materials on it?
- Will the scaffolding need to be tied in? How will this be done? Will the ties be moved as the work progresses?
- Is the scaffolding likely to be covered or enclosed as a protection against the elements? Is there provision for adding additional ties to the adjoining structure?
- What will be the method of access and egress? For example, a sloping ladder, vertical ladder, built-in stairway, or direct from the floors of the building structure?
- On a multi-level scaffolding, how many levels will be loaded with materials at one time? Will an engineer be required to make the calculations for the total anticipated loading and possibly design the scaffolding and the sills?
- If a rolling scaffolding is required, consider ground surface, height restriction (3 to 1 rule) hazards when moving (such as power lines, projections from the building, and potholes).
- Equipment inspection. You must inspect the equipment you plan to use to make sure that it is in good repair and suitable for the job. Check the following:
- Sills: suitable size and strength for the loads. Not split or rotten.
- Frames: no cracks in the welded joints. No kinks or dents in the top or bottom cross-members. Legs plumb and square with the cross-members. Brace locks in good working order. Coupling pins in place and secured to the frame.
- Cross braces and diagonal braces: straight with no bent ends. Pivot connection in good working order. No excessive rust.
- Scaffold planks: no split ends, saw cuts, notches, protruding nails, excessive warping. No contamination that may affect the integrity of the plank, such as oil, chemicals, and burns. (If you have any doubts about the strength of the plank, you may need to have it load-tested).
- All aluminium or with plywood deck platforms: not mis-shaped or cracked. Locks working. All bolts and screws in place. No burns or broken ends. If upper surface has non-skid coating, no rot or plywood separation on underside.
- Side or end brackets: hook-on attachment not distorted. No cracks in welds. No dents, kinks, or any signs of abuse.
- Guardrails: straight, with no kinks, dents, or excessive rust.
- Casters: same size and from same manufacturer. Wheel rotates well and the swivel below the stem is working. Brake mechanism works properly. Wheel tread has no damage.
- Levelling jacks: no cracks in weld where levelling jack is attached to the top of the caster. No thread damage. No curling or warping of the base plate. Adjusting nut is a tight fit.
- Other equipment: inspect any other equipment in the frame structure. Damaged equipment should be tagged and marked as not fit for use. Inform the supervisor so that others do not use it.
